トップ >
演算数と高速化 >
多重ループ > Sample 1: 共通項をループの外に(C)
多重ループ: Sample 1: 共通項をループの外に(C)
■ 概要
ここでは式(1)にしたがって配列rとθから2次元配列xの値を計算します。2次元配列だから、2重ループを使用して配列xを求めます。
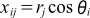
... 式(1)
Code 1では式(1)を素直にコーディングしたものです。メイン計算では2つのループ、ループiとループj、を設けてその中に式(1)の右辺をそのまま計算しています。
Code 1のメイン計算をよく観察すると、cos(theta[i])はループjの中で不変であることが解かります。ループjの中でcos(theta[i])が不変なのに、N回も繰り返し計算されることになります。cosの計算は重い計算のなので、できるだけ減らしたいものです。Code 1は無駄に重い計算を繰り返しているので、非常に遅いプログラムになります。
Code 1を改良したのはCode 2です。ループjの中で計算されていたcos(theta[i])を、ループjの外に出して、一時変数dに記憶しておきます。その後ループjの中でこの一時変数dを使えば、Code 1とまったく同じ結果が得られるはず。違いはcos(theta[i])を1回で済むので、Code 1よりCode 2の方がはるかに高速に計算できるはずです。
ここで用いた高速化手法は実はダミー変数を使用の一種です。繰り返し使用されている値をダミー変数に入れておいて、その後はダミー変数の値を参照するから、その値の計算は1回にすることができます。
■ ソースコード
|
◆ Code 1
|
◆ Code 2
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N 10000
double r[N], theta[N], x[N][N];
int main()
{
int i,j;
// Initialization
for (i=0; i<N; i++) r[i] = rand();
for (i=0; i<N; i++) theta[i] = rand();
// Start time
clock_t time0 = clock();
// Main calculation
for (i=0; i<N; i++) {
//
for (j=0; j<N; j++) {
x[i][j] = r[j] * cos(theta[i]);
}
}
// Finish time
clock_t time1 = clock();
// Output time
double time = (double)(time1-time0)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("Time = %15.7f sec\n", time);
return 0;
}
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N 10000
double r[N], theta[N], x[N][N];
int main()
{
int i,j;
// Initialization
for (i=0; i<N; i++) r[i] = rand();
for (i=0; i<N; i++) theta[i] = rand();
// Start time
clock_t time0 = clock();
// Main calculation
for (i=0; i<N; i++) {
double d = cos(theta[i]);
for (j=0; j<N; j++) {
x[i][j] = r[j] * d;
}
}
// Finish time
clock_t time1 = clock();
// Output time
double time = (double)(time1-time0)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("Time = %15.7f sec\n", time);
return 0;
}
|
■ 計算時間の測定結果
Code 1とCode 2の計算時間の測定結果を表1に示します。ここではそれぞれのコードを5回実行して、平均とCode 1とCode 2との計算時間の比率も表示します。
表1 計算時間の測定結果(単位: sec)
|
1回目 |
2回目 |
3回目 |
4回目 |
5回目 |
平均 |
倍率 |
| Code 1 |
4.32 |
4.31 |
4.46 |
4.31 |
4.29 |
4.34 |
9.59 |
| Code 2 |
0.42 |
0.45 |
0.47 |
0.45 |
0.47 |
0.45 |
- |
■ 考察
Code 2はCode 1に比べて10倍弱速いという結果が得ました。配列のサイズNが大きければさらに倍率が大きくなるでしょう。
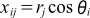 ... 式(1)
... 式(1)
